Move Fast. Implement Smart.
Cloobot automates requirement gathering, user story creation, and delivery planning — helping teams move from discovery to dev in record time.
Book a DemoThe Parts of Implementation Everyone Dreads - Automated.

Metadata-powered intelligence
Cloobot scans your org's setup to assess the current state, uncover inefficiencies, and recommend improvements, so you can reduce technical debt and build with confidence.
Context - Aware Documentation
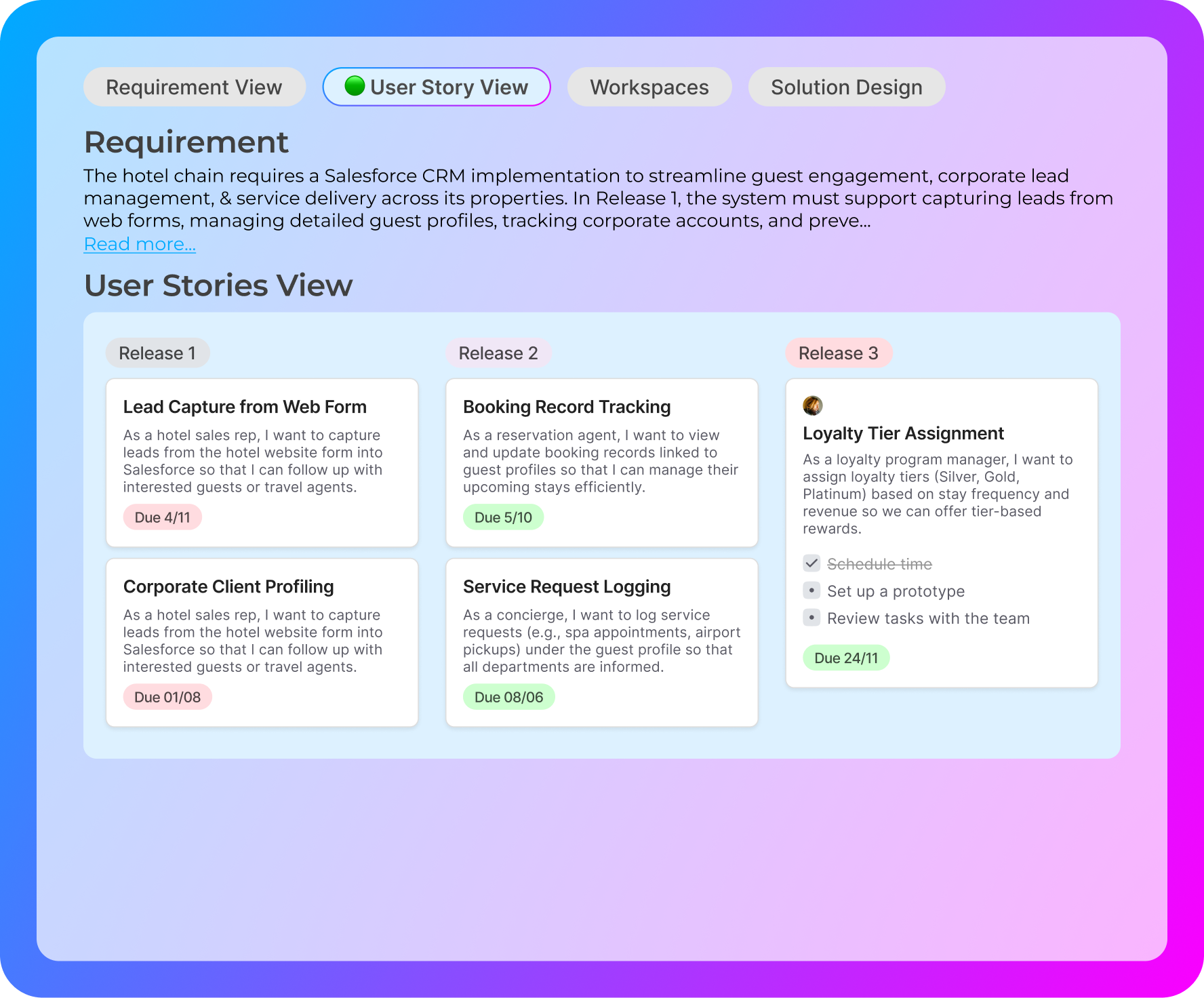
Automatically generates & maintains requirements, user stories with acceptance criteria, & builds task breakdowns, versioned, context-aware, & always up to date as your project evolves.

Seamless integration
Effortlessly connects with your existing tools and workflows for a frictionless experience.
What Our Partners are Saying
"Partnering with Cloobot has fundamentally changed how we approach Salesforce delivery. What used to take weeks now happens in hours - without compromising quality."
"Cloobot significantly simplifies handling Salesforce requirements. It can transform BRD document into a comprehensive solution design, task-level design and perform gap analysis with 70-80% accuracy"
AI Agents, Real Delivery.
BA Agent
Captures business requirements with precision, turning conversations, notes, or inputs into complete, traceable specs including user stories and acceptance criteria. Never miss a detail, and reduce the discovery cycle by 50%.
Architect Agent
Analyzes org metadata, maps dependencies, and auto-generates scalable, implementation-ready designs. From task breakdowns to solution blueprints, the Architect Agent brings clarity before the first line of config.
Testing Agent
Auto-generates test scripts based on requirements and user stories, accelerating QA handoff and reducing bugs from day one. Ensure that what gets built matches what was asked.